The Benchmark Dollar Rates for Global Finance (The Hierarchy of Dollar Rates)
The Benchmark Dollar Rates for Global Finance (The Hierarchy of Dollar Rates)
The Global Dollar Rates Hierarchy is a detailed structure outlining various USD rates in the financial markets, categorized based on their specific purposes and the entities involved.
This is the hierarchy of dollar rates…Thank you
for this idea.The Fed’s Overnight Reverse Repo Rate (ON RRP)
ON RRP1 acts as a sub-floor for the private dollar rates. This rate is used by financial institutions to deposit excess reserves overnight with the Federal Reserve, earning a specified interest rate. ( %5.30, 18 June 2024)
The Fed’s FRP (Foreign Repo Pool) Rate (FRPR)(FIMA reverse repo)
FRPR2 serves as the floor for international dollar rates. This facility3 is overnight reverse repurchase agreement (the FIMA reverse repo pool) with the foreign central banks, monetary authorities, and international organizations. The FIMA reverse repo pool is a short-term U.S. dollar money-market investment that also supports account holders’ daily cash management needs related to the settlement of payments and securities transactions. Account holders that opt to participate in the FIMA reverse repo pool instruct the New York Fed to invest certain end-of-day cash balances in an overnight repurchase agreement under which securities are purchased from the Federal Reserve’s System Open Market Account (SOMA). At maturity, on the following business day, the securities are repurchased by the SOMA at a repurchase price that includes a return calculated at a rate generally equivalent to the New York Fed’s overnight reverse repurchase operations (ON RRP).
The Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR)
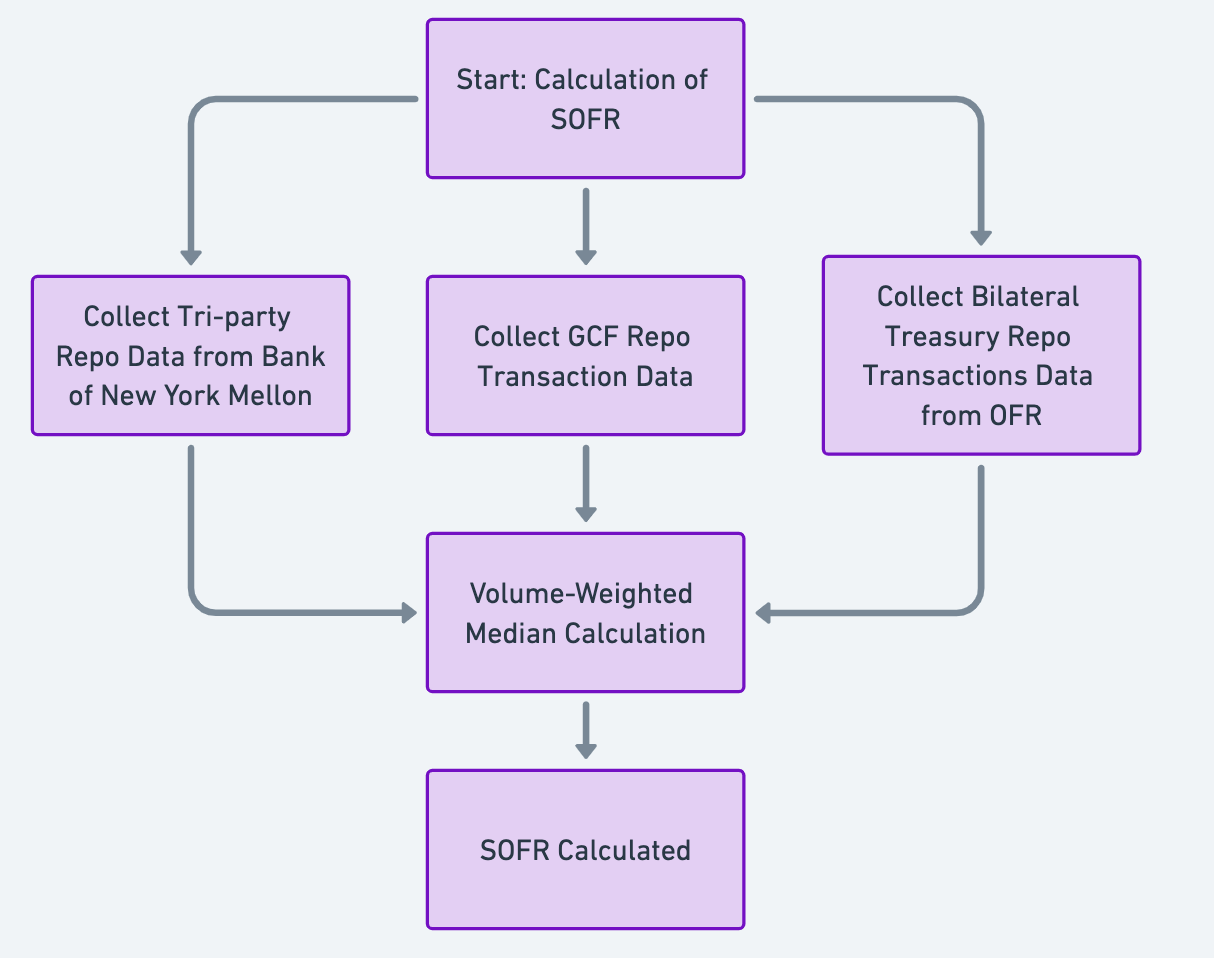
SOFR4 is a broad measure of the cost of borrowing cash overnight collateralized by Treasury securities. The SOFR includes all trades in the Broad General Collateral Rate plus bilateral Treasury repurchase agreement (repo) transactions cleared through the Delivery-versus-Payment (DVP) service offered by the Fixed Income Clearing Corporation (FICC), which is filtered to remove a portion of transactions considered “specials”. ( %5.33, 18 June 2024)
The Federal Funds Rate
The Federal Reserve (Fed) defines this concept as “The federal funds rate is the interest rate at which depository institutions trade federal funds (balances held at Federal Reserve Banks) with each other overnight”. The federal funds are depository institutions’ reserve balances with Federal Reserve Banks. The federal funds rate is determined by ranking all financial institutions that have an account at the Fed, taking the volume of funds exchanged during the day as a criterion, and selecting the interest rate available in the median of these transactions. It is called as Effective Federal Funds Rate5. ( %5.33, 18 June 2024)
The Interest Rate on Reserve Balances(IORB)
The interest rate on reserve balances (IORB rate) is the rate of interest that the Federal Reserve pays on balances maintained by or on behalf of eligible institutions in master accounts at Federal Reserve Banks. Starting July 29, 2021, the interest rate on excess reserves (IOER) and the interest rate on required reserves (IORR) were replaced with a single rate, the interest rate on reserve balances (IORB)6. ( %5.40, 18 June 2024)
The Discount Rate
The term of the Discount Rate covers the four different lending tools. These are Primary Credit Secondary Credit Seasonal Credit and Emergency Credit. It is usually used the primary credit as the discount rate.
The Standing Repo Facility Rate
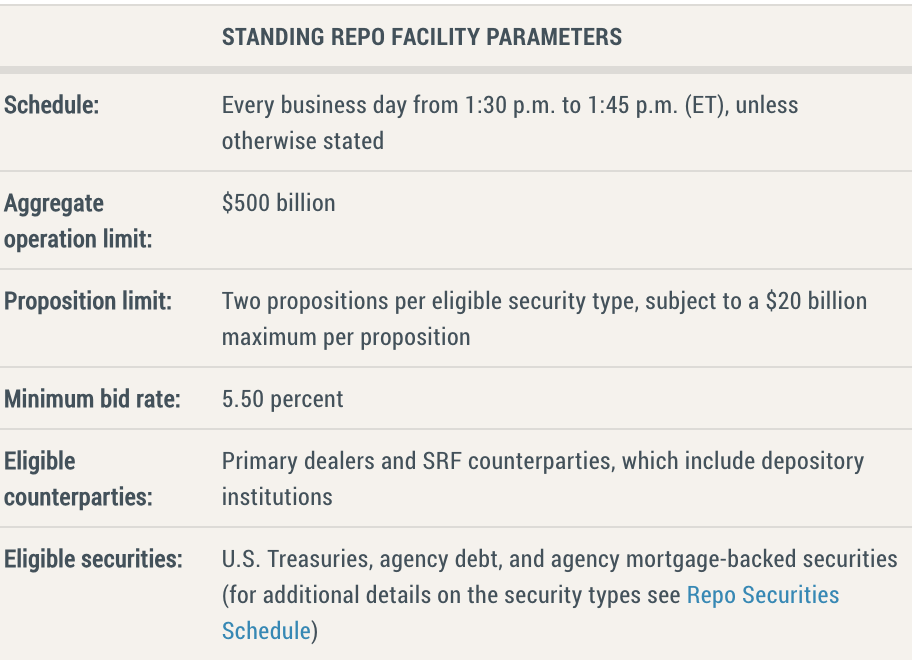
In July 2021, the Fed added to its implementation toolkit, announcing the establishment of a domestic standing repurchase agreement (repo) facility (SRF). The SRF serves as a backstop in money markets to support the effective implementation of monetary policy and smooth market functioning. It does so by limiting the potential for occasional pressures in overnight interest rates to push the effective federal funds rate (EFFR) above the FOMC’s target range.7 Banks are key participants in the fed funds market and adding them as SRF counterparties should enhance rate control by providing a backstop source of liquidity against high-quality assets. As such, the SRF serves as a complement to the discount window. As a backstop facility, the SRF is only intended to be used intermittently when stress emerges in funding markets and overnight interest rates are pressured higher, as noted in this speech by System Open Market Account (SOMA) manager Lorie Logan8 . (min %5.50, 18 June 2024)
These rates form the foundation of the broader dollar rate structure, influencing the cost of borrowing and lending in world dollar market. They provide stability and predictability, ensuring that financial institutions can manage their short-term funding needs efficiently. Next, we will explore the rates that build upon the secured rates , further up the hierarchy in the Global Dollar Rates framework.
Treasury Par Yield Curve Rates
These rates are commonly referred to as "Constant Maturity Treasury(CMT)" rates. Yields are interpolated by the Treasury from the daily par yield curve. This curve, which relates the yield on a security to its time to maturity, is based on the closing market bid prices on the most recently auctioned Treasury securities in the over-the-counter market. These par yields are derived from indicative, bid-side market price quotations (not actual transactions) obtained by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York at or near 3:30 PM each trading day. The CMT yield values are read from the par yield curve at fixed maturities, currently 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 months and 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 20, and 30 years. This method provides a par yield for a 10-year maturity, for example, even if no outstanding security has exactly 10 years remaining to maturity.9
The FX Swap Rate
An FX swap involves two parties exchanging currencies (e.g., euros for dollars) and agreeing to reverse the transaction at a future date at a pre-agreed exchange rate. It allows entities to borrow dollars short-term while lending an equivalent amount in another currency, hedging against exchange rate risk. The most traded FX swap pairs are dollar-euro and dollar-yen, the majority of FX swap trading takes place in the UK and dealer banks are increasingly entering into swap agreements with non-dealer counterparties.10
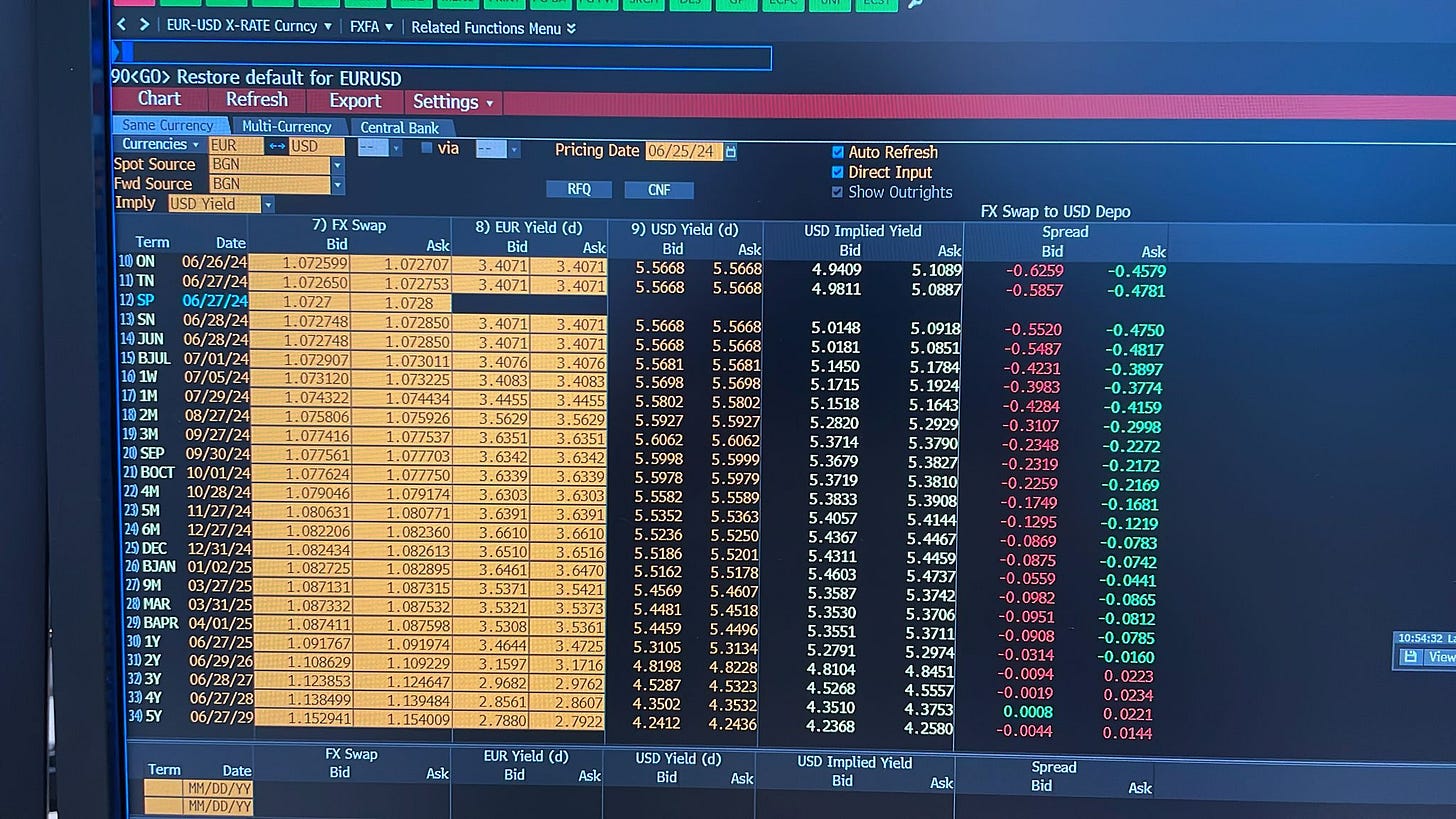
You can see Bloomberg EUR/USD FXFA<go> page attached below
EUR 3 months yield=3.9412
US 3 months yield= 5.6683
Spot Rate: 1.0580
USD ımplied yield was greater than US yield and spread was the positive. This means that the FX swap way of getting US dollars is expensive compared to the cost of borrowing dollars in unsecured markets.
This is new and fresh Bloomberg EUR/USD FXFA page in 25 June 2024.
Thanks to Ahmet Baran.
Foreign and International Monetary Authorities (FIMA) Repo Facility
The Federal Reserve established a repurchase agreement facility for foreign and international monetary authorities (FIMA Repo Facility). By creating a backstop source of temporary dollar liquidity for FIMA account holders, the facility can help address pressures in global dollar funding markets that could otherwise affect financial market conditions in the United States. Its role as a liquidity backstop also helps to support the smooth functioning of financial markets more generally.
The FIMA Repo Facility allows FIMA account holders, which consist of central banks and other international monetary authorities with accounts at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, to enter into repurchase agreements with the Federal Reserve. In these transactions, approved FIMA account holders temporarily exchange their U.S. Treasury securities held with the Federal Reserve for U.S. dollars, which can then be made available to institutions in their jurisdictions. This facility provides, at a backstop rate, an alternative temporary source of U.S. dollars for foreign official holders of Treasury securities other than sales of the securities in the open market.11
Central Bank Liquidity Swaps
The Federal Reserve has entered into agreements to establish central bank liquidity swap lines with a number of foreign central banks. The swap lines are designed to improve liquidity conditions in dollar funding markets in the United States and abroad by providing foreign central banks with the capacity to deliver U.S. dollar funding to institutions in their jurisdictions during times of market stress.12
The Eurodollar Rates
A Eurodollar is a U.S. dollar deposited in banks outside the United States. These deposits are not subject to U.S. banking regulations, making them a part of the international financial market. Eurodollars are used in international trade and finance due to their flexibility and accessibility, and they often earn higher interest rates compared to domestic deposits due to the different regulatory environment. You can see eurodollar rates from here (1991-2024).13 Don’t forget that SOFR is new LIBOR.14
Conclusion
The Global Dollar Rates Hierarchy provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the various USD rates and their roles in the financial markets. These rates form the foundation of the broader dollar rate structure, influencing borrowing and lending costs worldwide. They offer stability and predictability, enabling financial institutions to manage short-term funding needs effectively. By understanding these rates, market participants can better navigate the complexities of the global dollar market.
Engin YILMAZ (
)








Sweet Mother Mary. What an incredible post. I’ll try to come back and study it periodically, but boy do I have a long way to go…