Understanding the Swap Curve(A Practical Guide to Understanding Swap Curve Jargon)
From Wall Street to Main Street: How the Swap Curve Affects Your Wallet Strategies for Profiting from Swap Rate Fluctuations Understanding the Swap Curve: Implications and Analysis #swapcurve
Hey there, finance enthusiasts! Ever heard of the "swap curve" and felt like it belonged in a secret language reserved for Wall Street wizards?
Well, fear not, for today we're demystifying this beast one term at a time!
Prepare to navigate the world of interest rates with newfound confidence, whether you're a seasoned investor or just dipping your toes into the financial pool.
What is the swap rate?
Interest rate swaps are an integral part of the fixed-income market. These derivative contracts, which typically exchange, or swap, fixed-rate interest payments for floating- rate interest payments, are an essential tool for investors who use them for speculation or hedging risk. The size of the payments reflects the floating and fixed rates, the amount of principal and the maturity of the swap. The interest rate for the fixed-rate leg of an interest rate swap is known as the swap rate.1
Floating rates are based on some short-term reference interest rate, such as three-month or six- month dollar SOFR; other reference rates include euro-denominated Euribor (European Interbank Offered Rate) and yen-denominated Tibor (Tokyo Interbank Offered Rate).
The fixed interest rates are calculated automatically when the floating interest rates are known. You can see how this is done from the link below.
What is the swap spread?
The difference between the swap rate and the equivalent government bond yield for the same maturity.2
What is the swap curve?
The yield curve of swap rates is called the swap rate curve, or, more simply, the swap curve. The swap market is a highly liquid market for three reasons. First, unlike bonds, a swap does not have multiple borrowers or lenders, only counterparties who exchange cash flows. Such arrangements offer significant flexibility and customization in the swap contract’s design. Second, swaps provide one of the most efficient ways to hedge interest rate risk. Third, many countries do not have a liquid government bond market with maturities longer than one year. The swap curve is a necessary market benchmark for interest rates in these countries.3
USD SOFR swaps are used for saving on interest expense, supporting liquidity and maintaning cash hedge.
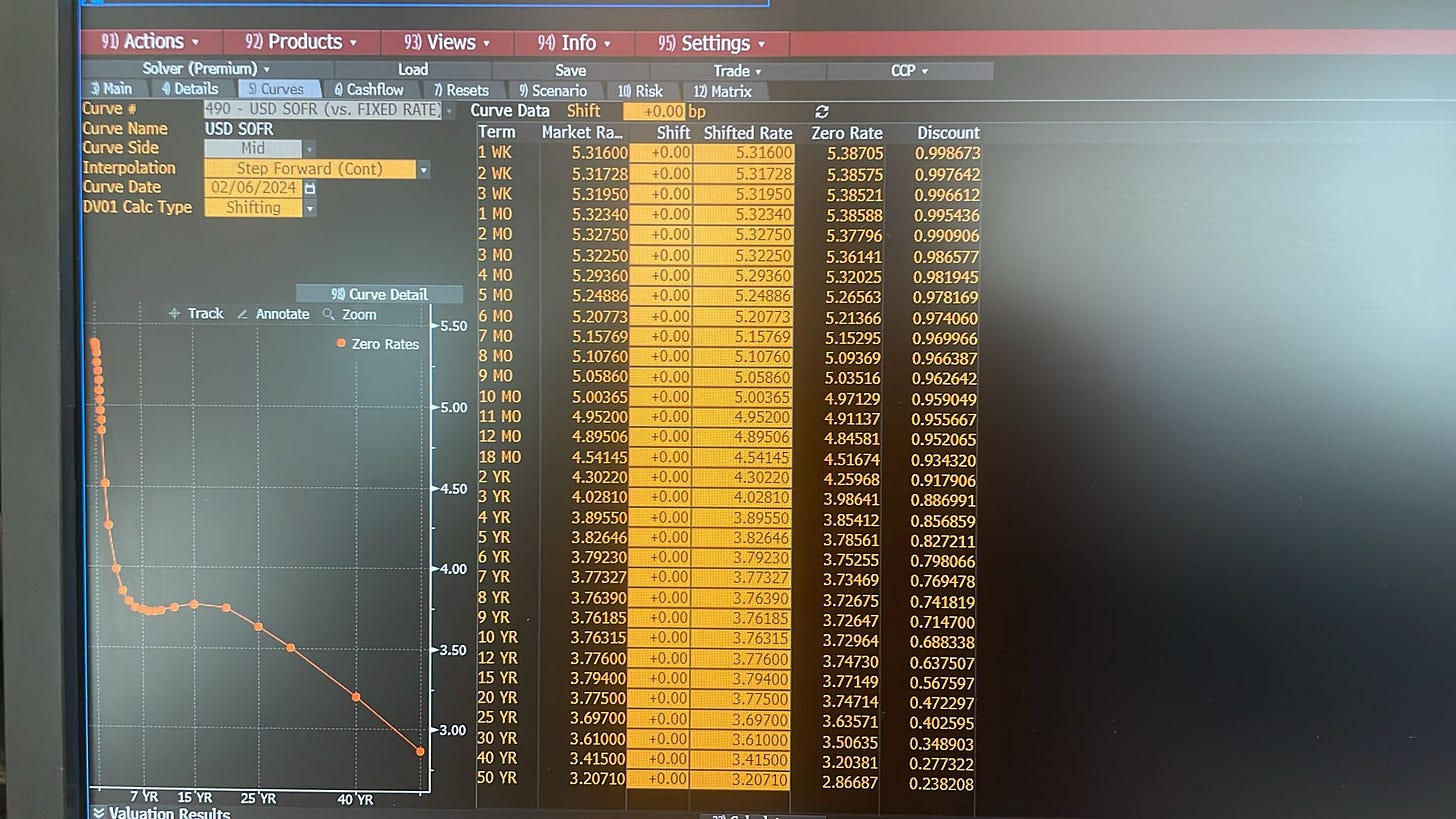
This graph is taken from the Bloomberg terminal (490- USD SOFR) on February 6, 2024, and it shows the USD SOFR zero rates in the “Zero Rate” column.
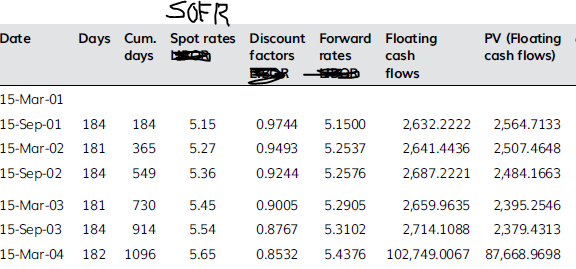
These are really the spot rates4 (yield curve). The forward rates, floating cash flows and swap rates are calculated from these rates.
USD SOFR Fixed/Float swaps screen in the terminal gives the fixed market quotes for the each tenor. These rates(Mid ticks) are same as “Market Rates” in the first screen.
This is my github page. I prepare short code which it shows SOFR zero rate calculation from the market rates.
There is a also good example here5 how sofr swap curve uses in terminal.
Engin YILMAZ (
)Sources
The Term Structure and Interest Rate Dynamics by Thomas S.Y. Ho, PhD, Sang Bin Lee, PhD, and Stephen E. Wilcox, PhD, CFA Thomas S.Y. Ho, PhD, (2010), Link
The Term Structure and Interest Rate Dynamics by Thomas S.Y. Ho, PhD, Sang Bin Lee, PhD, and Stephen E. Wilcox, PhD, CFA Thomas S.Y. Ho, PhD, (2010), Link
Derivatives: Theory and Practice, Keith Cuthbertson, Dirk Nitzsche, Niall O'Sullivan (Page:591)
https://rateslib.readthedocs.io/en/latest/z_swpm.html#cook-swpm-doc